Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. It can cause swelling, pain, and redness, and may lead to serious complications if the clot travels to the lungs, resulting in a pulmonary embolism. DVT is often caused by long periods of immobility, surgery, injury, or certain medical conditions. Treatment includes blood thinners, compression stockings, and in severe cases, clot-dissolving medications. Early diagnosis and prevention are key to avoiding life-threatening outcomes.
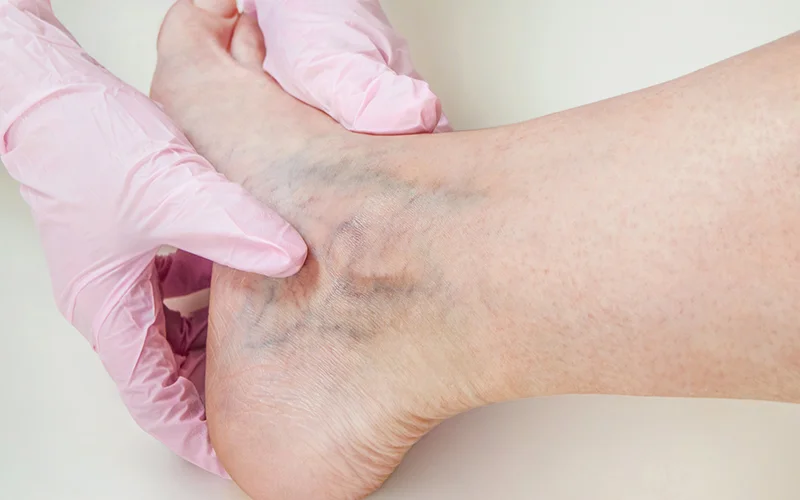
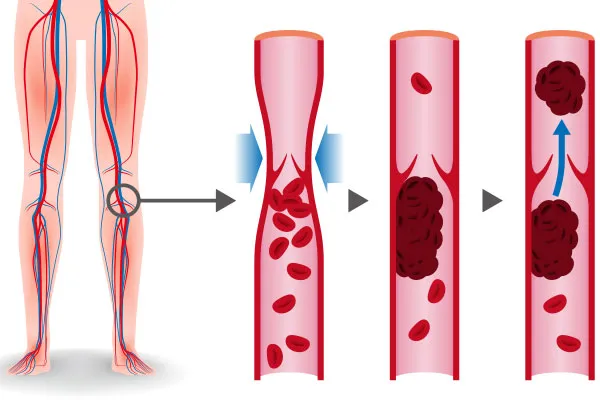
DVT symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common signs include:
Often in one leg, particularly around the calf or thigh.
The pain may feel like cramping or soreness in the affected leg.
The skin over the affected area may become red or bluish in colour.
The leg may feel warmer than the rest of the body.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s essential to seek immediate treatment for deep vein thrombosis to reduce the risk of complications.
DVT can occur due to several factors, including:
Surgery or physical trauma may damage a vein, which can result in a deep vein blood clot.
Compared to older vein-stripping methods, this is less invasive and ensures quicker healing.
Certain health conditions, such as cancer or heart disease, increase the risk of DVT disease.
Increased pressure on pelvic veins and hormonal changes can raise clot risk.
Birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy can increase clotting.